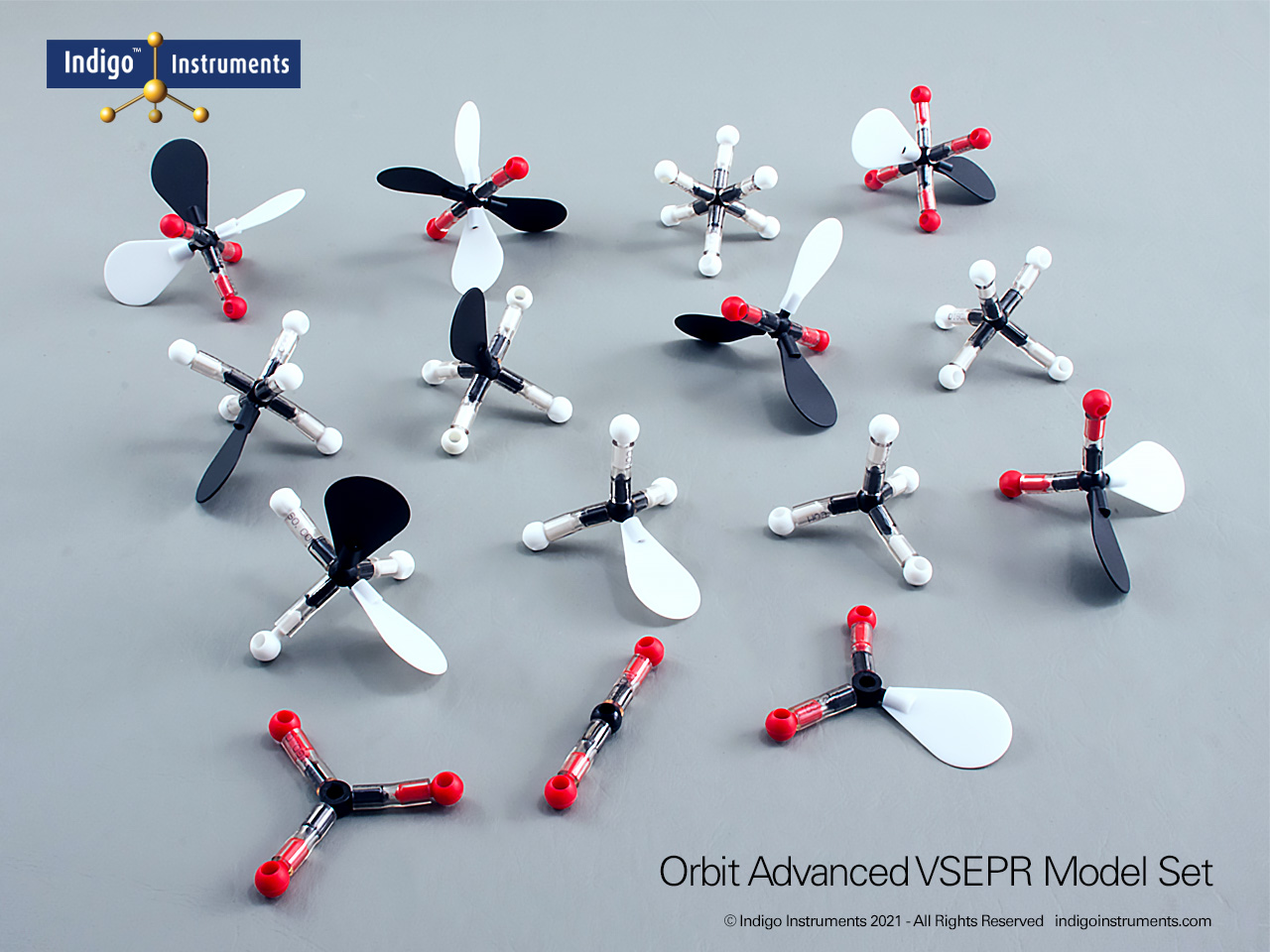
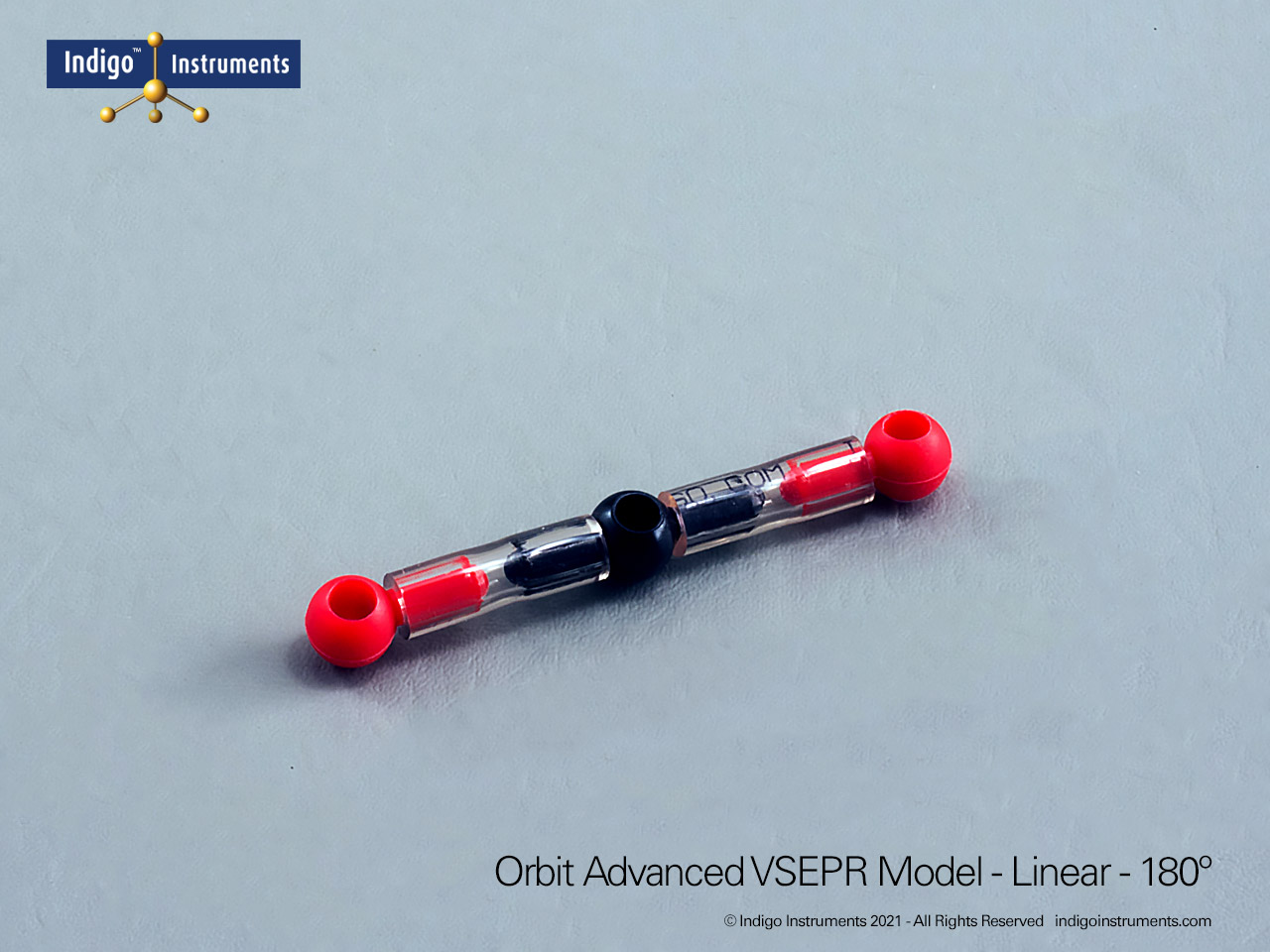
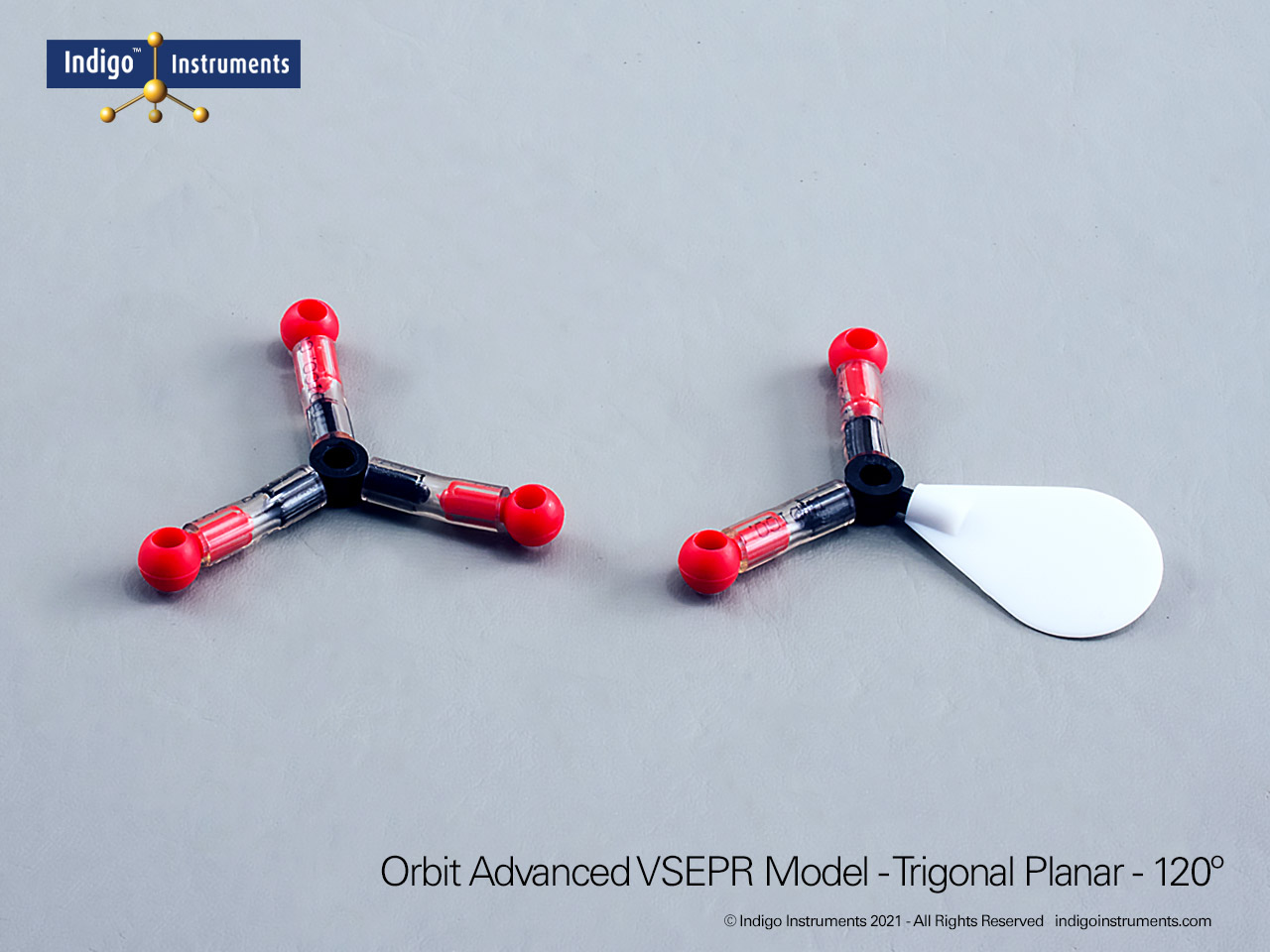
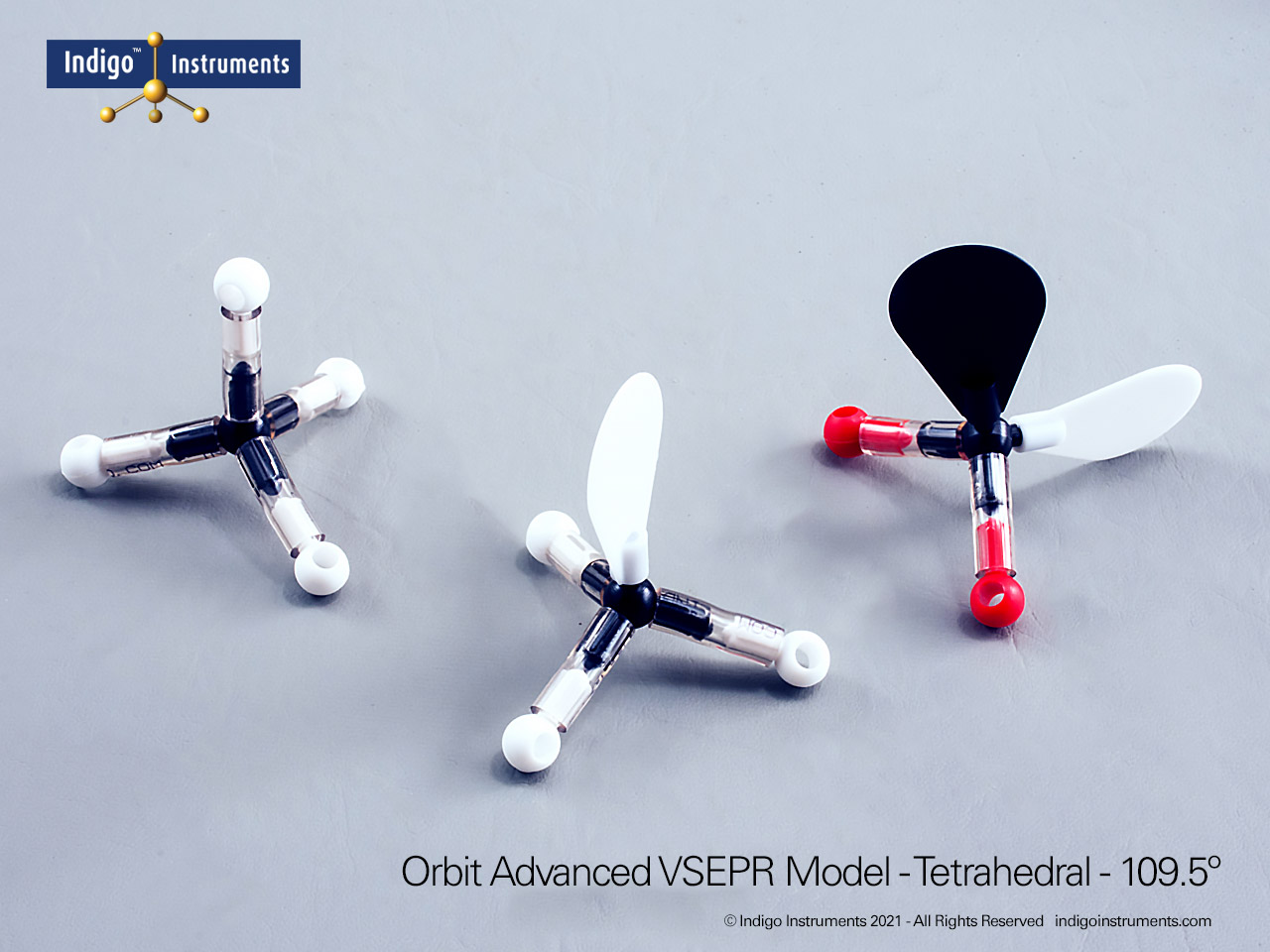
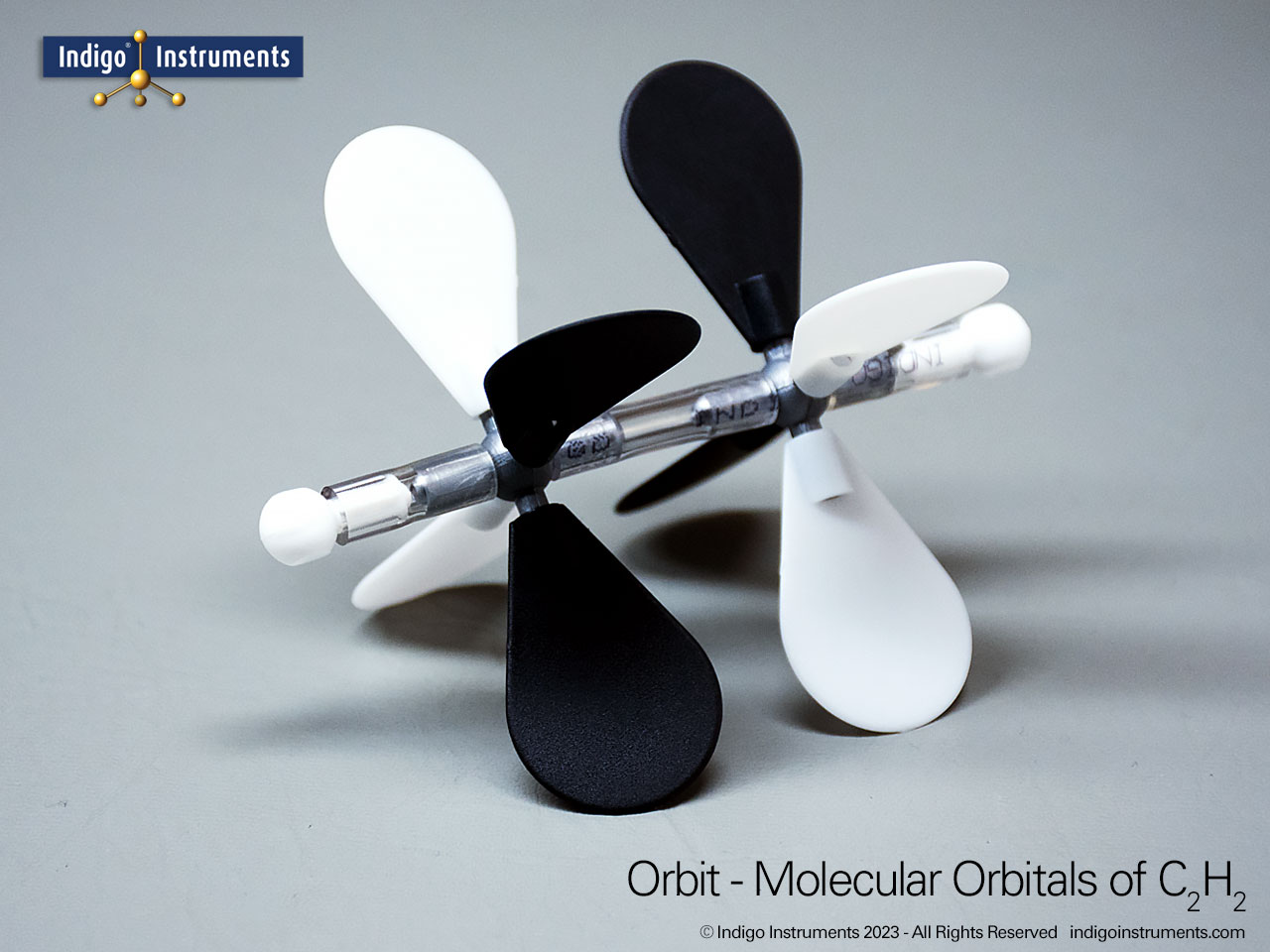
VSEPR Theory Polarity/Dipole Models
SKU: 68823W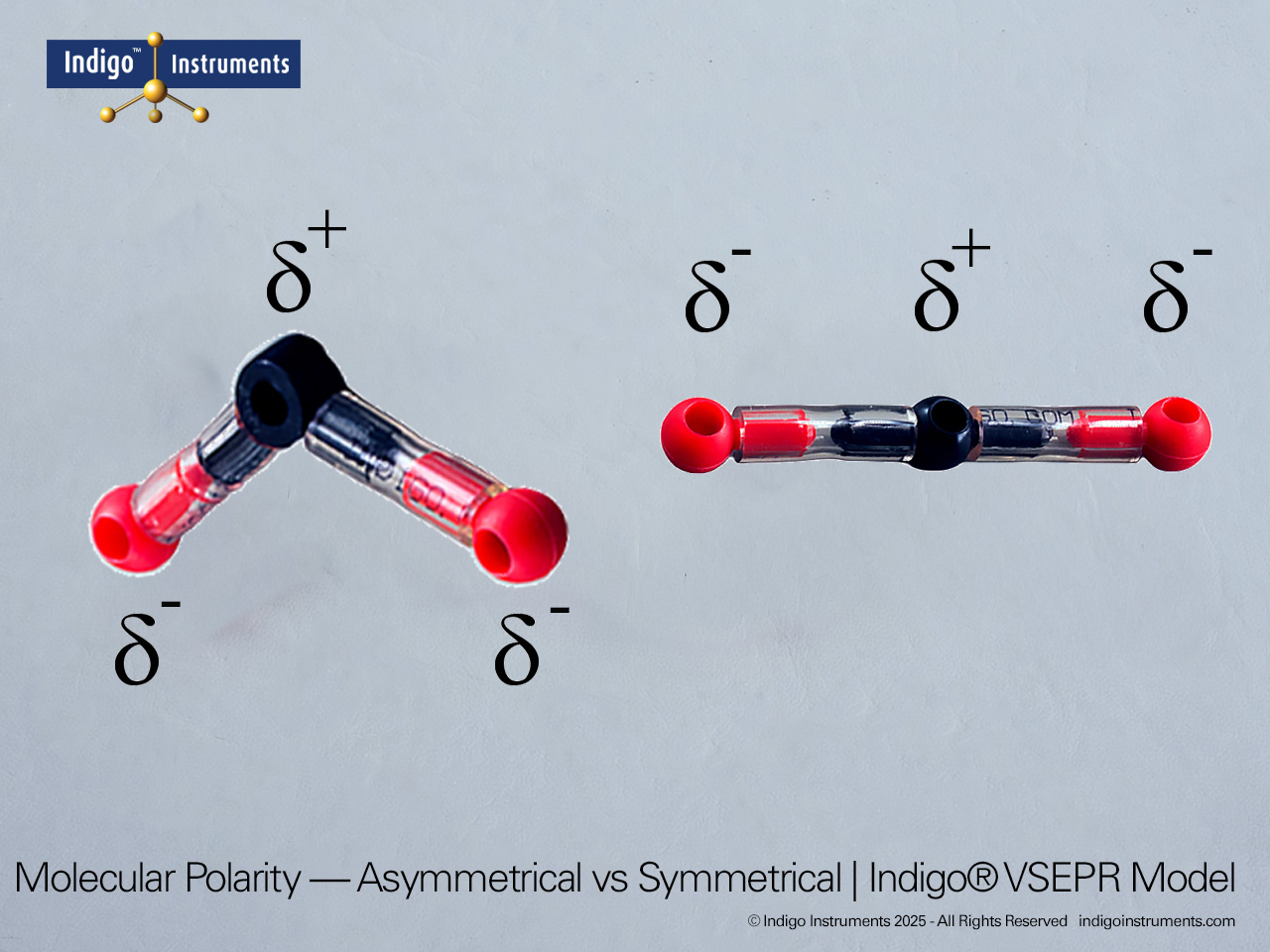
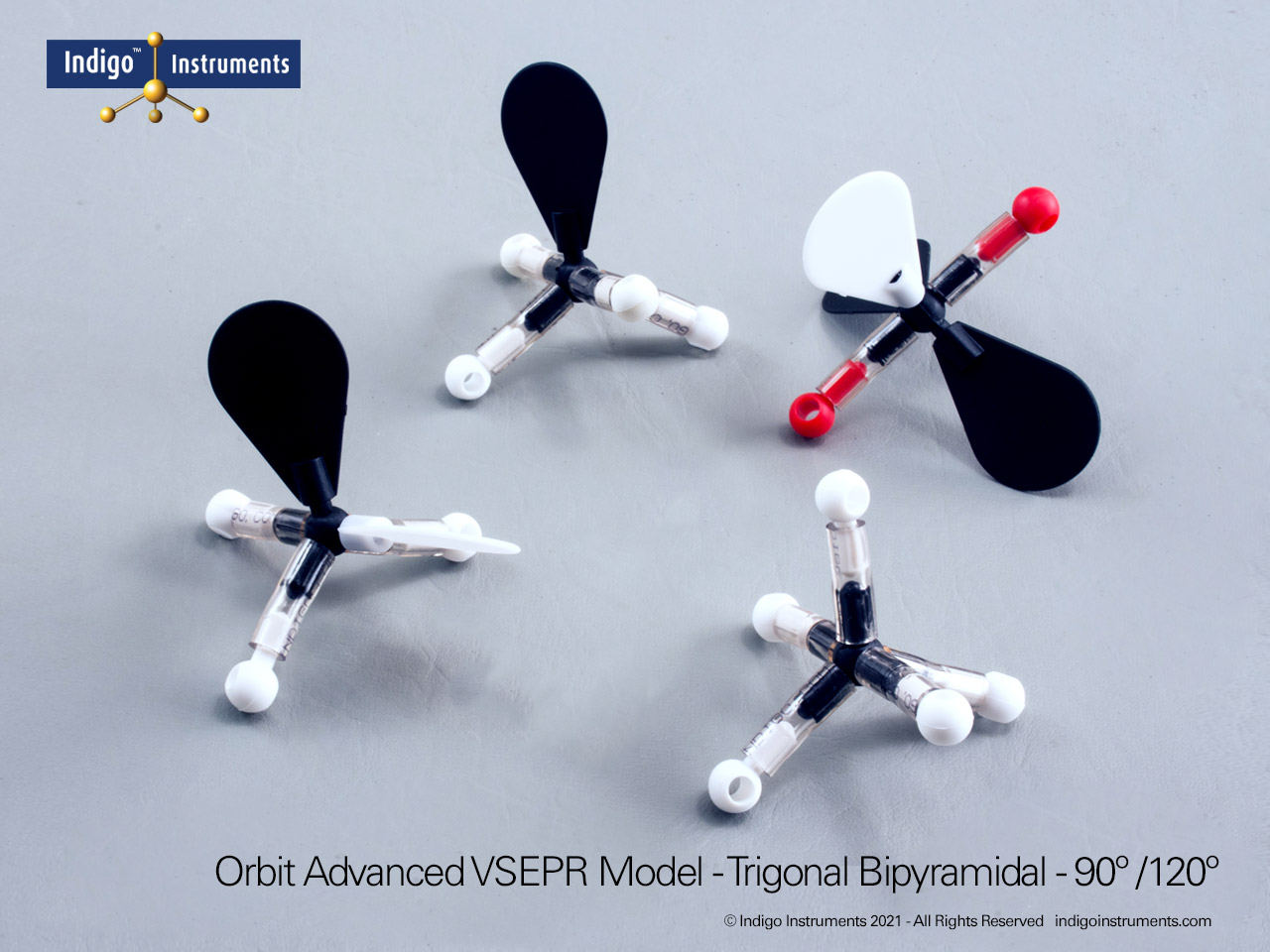
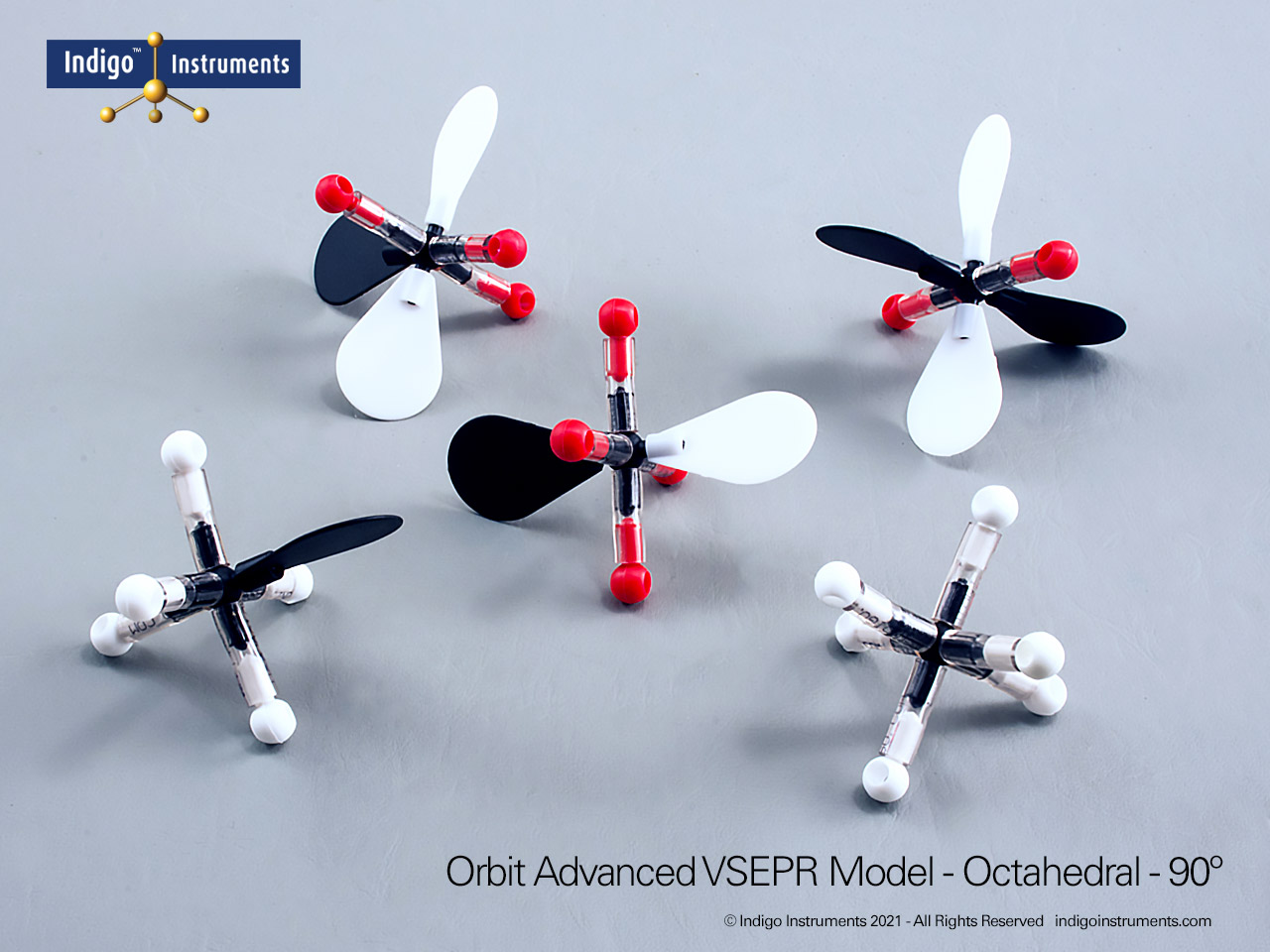
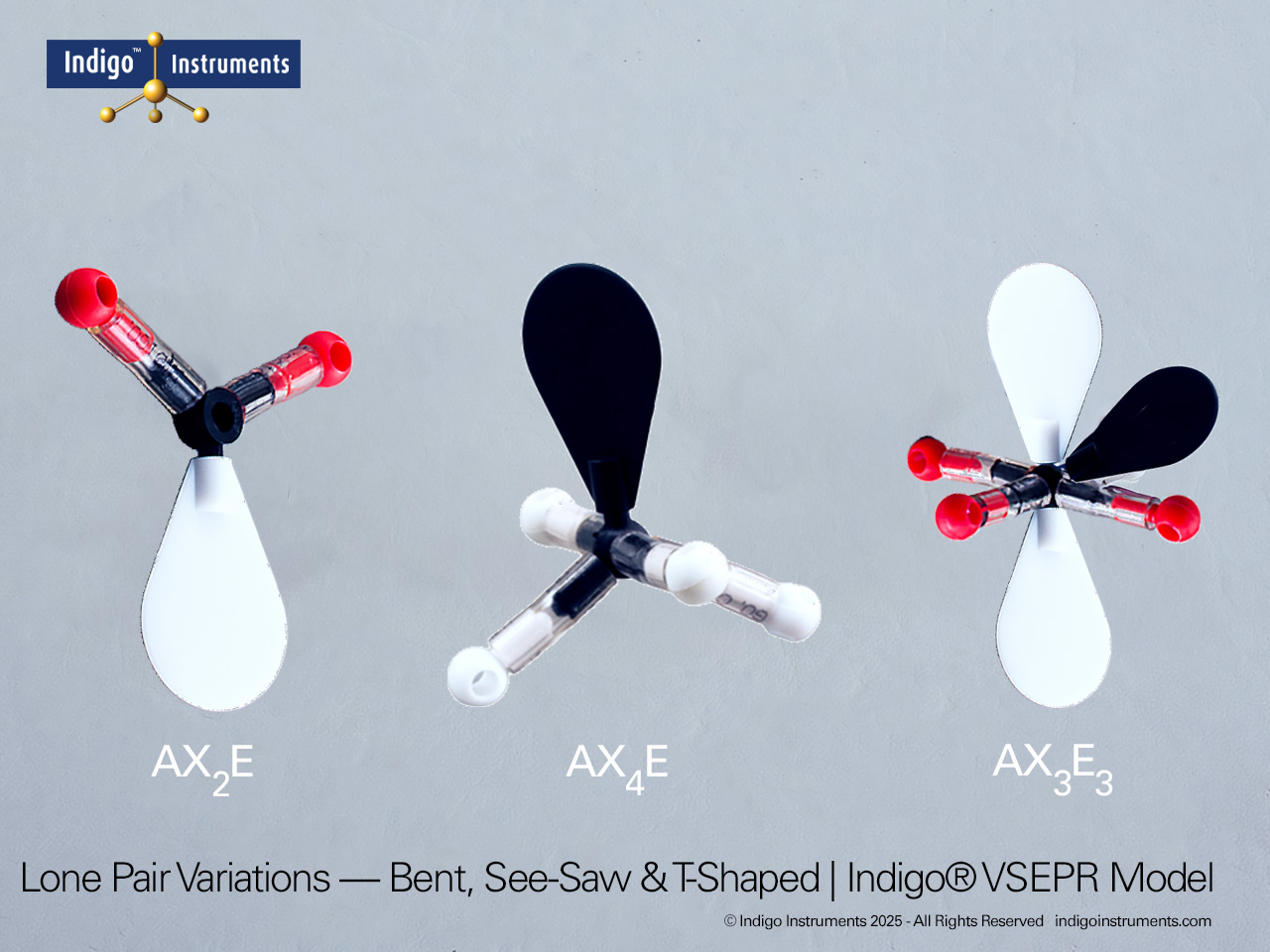
Understand how molecular geometry determines polarity with Indigo® VSEPR theory models. Explore polar vs nonpolar shapes like H2O (MgCl2), CO2, and PF5.
Explore how molecular geometry controls polarity using Indigo® VSEPR Models. By comparing symmetrical and asymmetrical shapes, students can visualize how bond dipoles either cancel or reinforce each other. This hands-on study makes abstract polarity concepts tangible, linking geometry, electronegativity, and molecular symmetry.