Advanced VSEPR Theory Molecular Model Kit
SKU: 68823W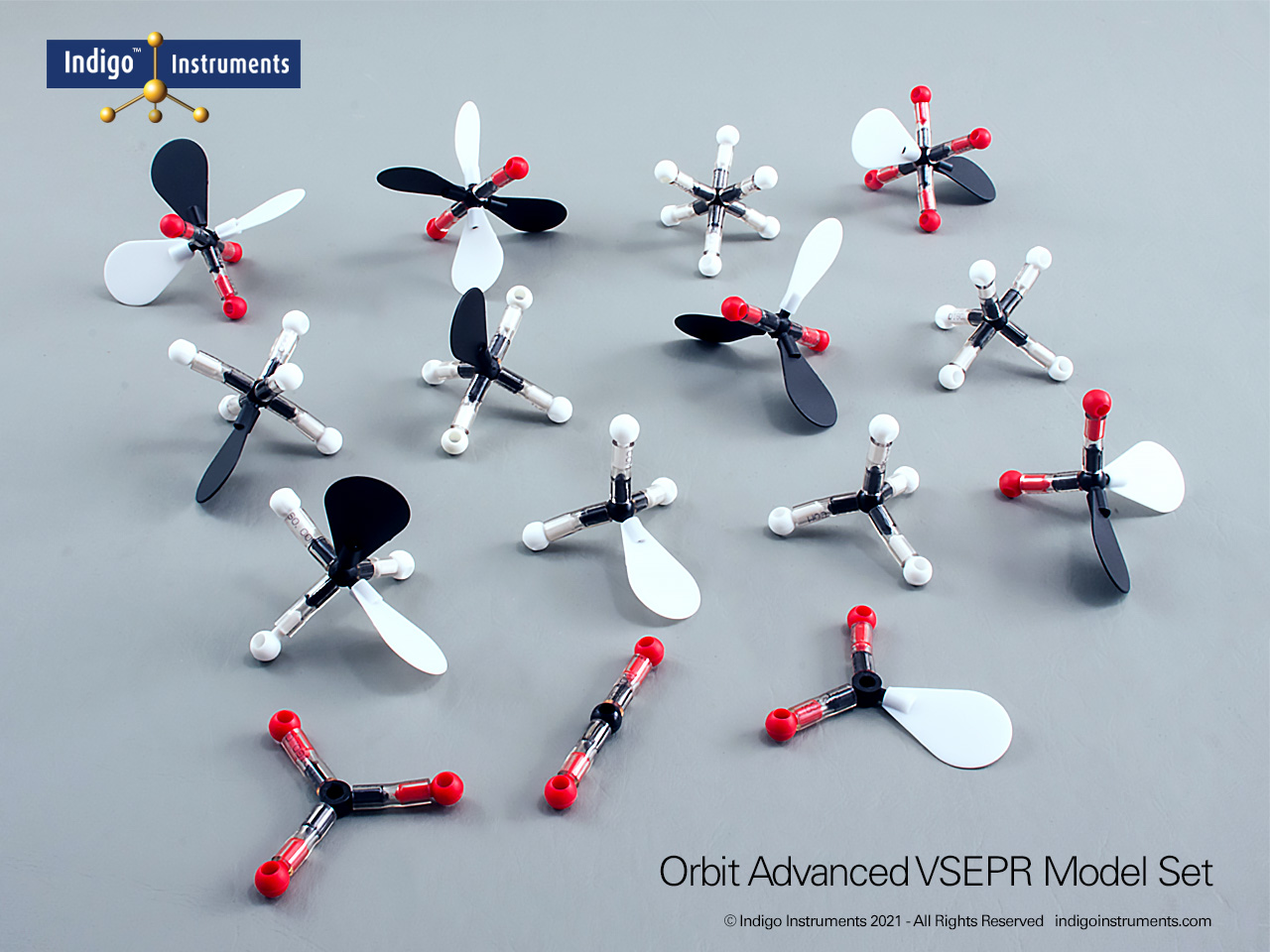
Explore 15 molecular geometries with Indigo®’s VSEPR theory model kit. Perfect for chemistry classes & labs studying shape, polarity, and bonding theory.
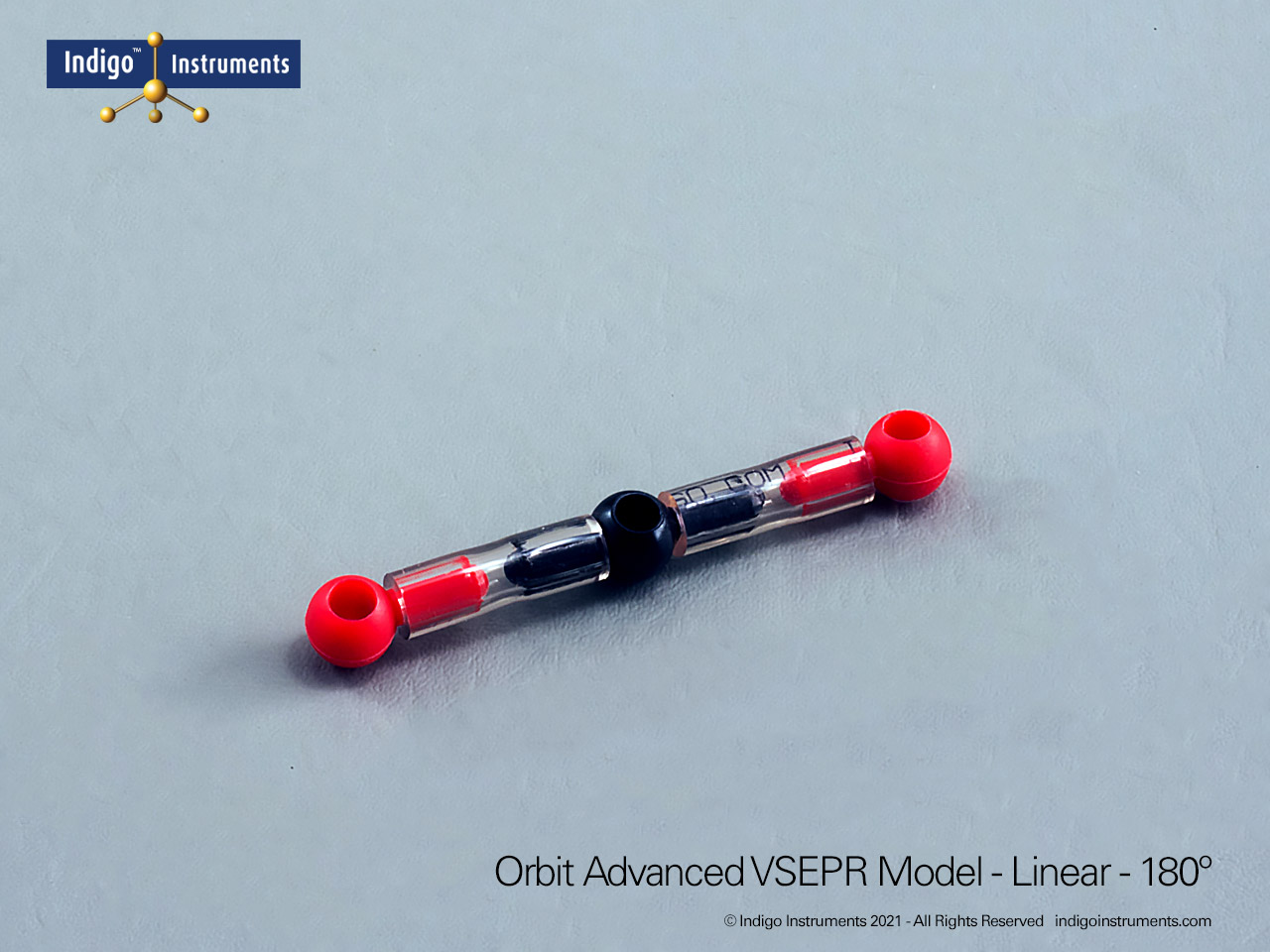
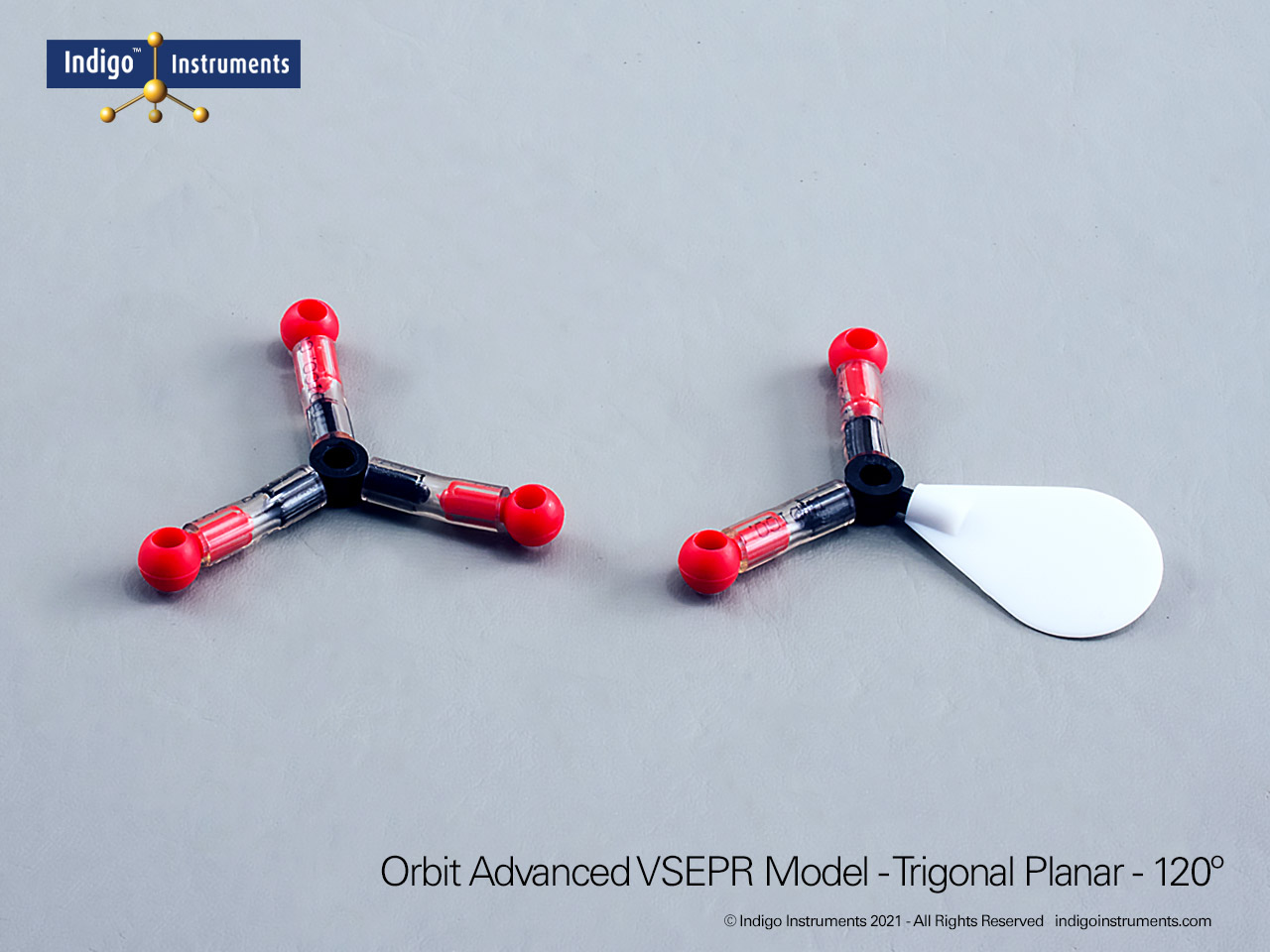
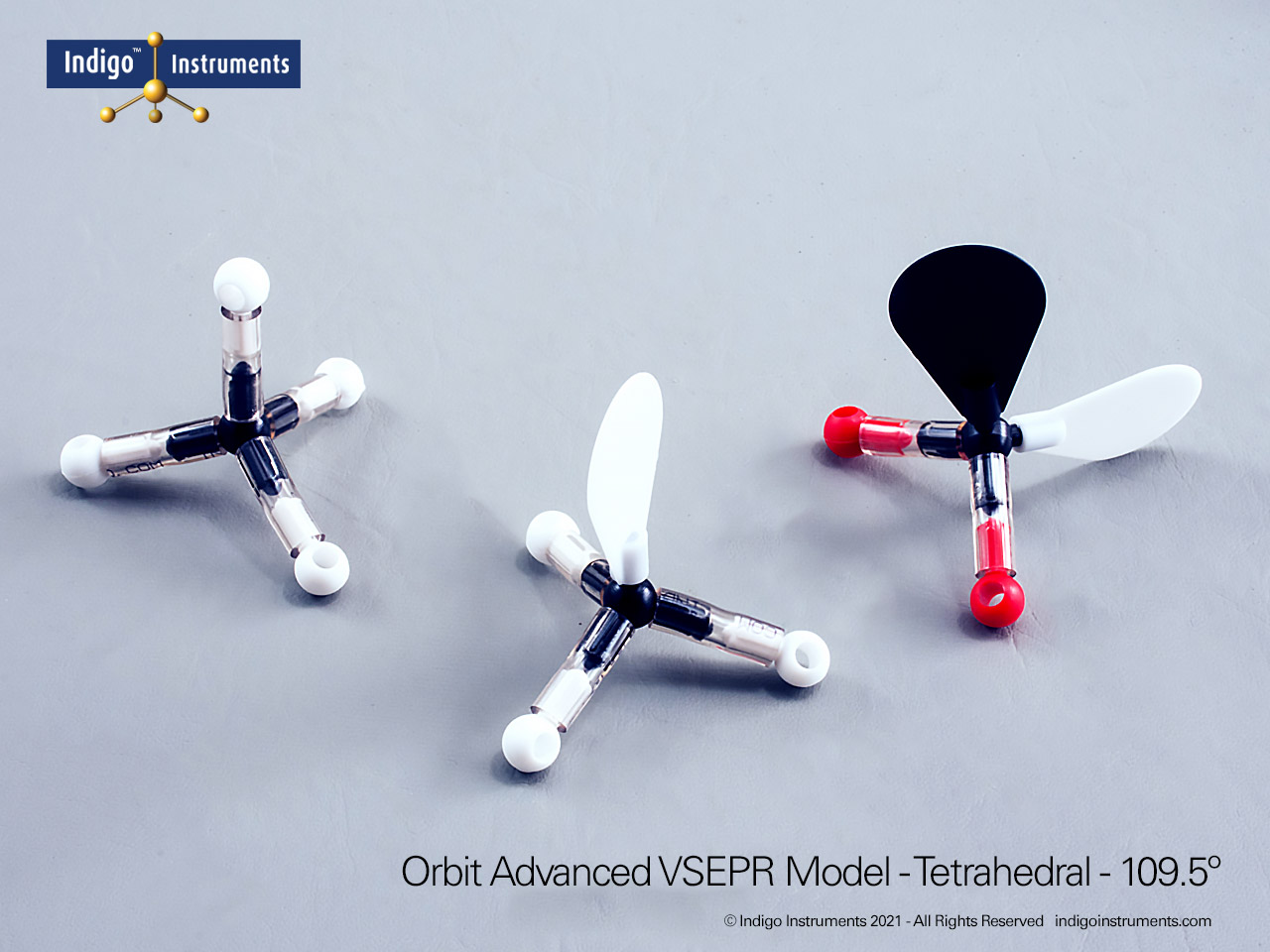
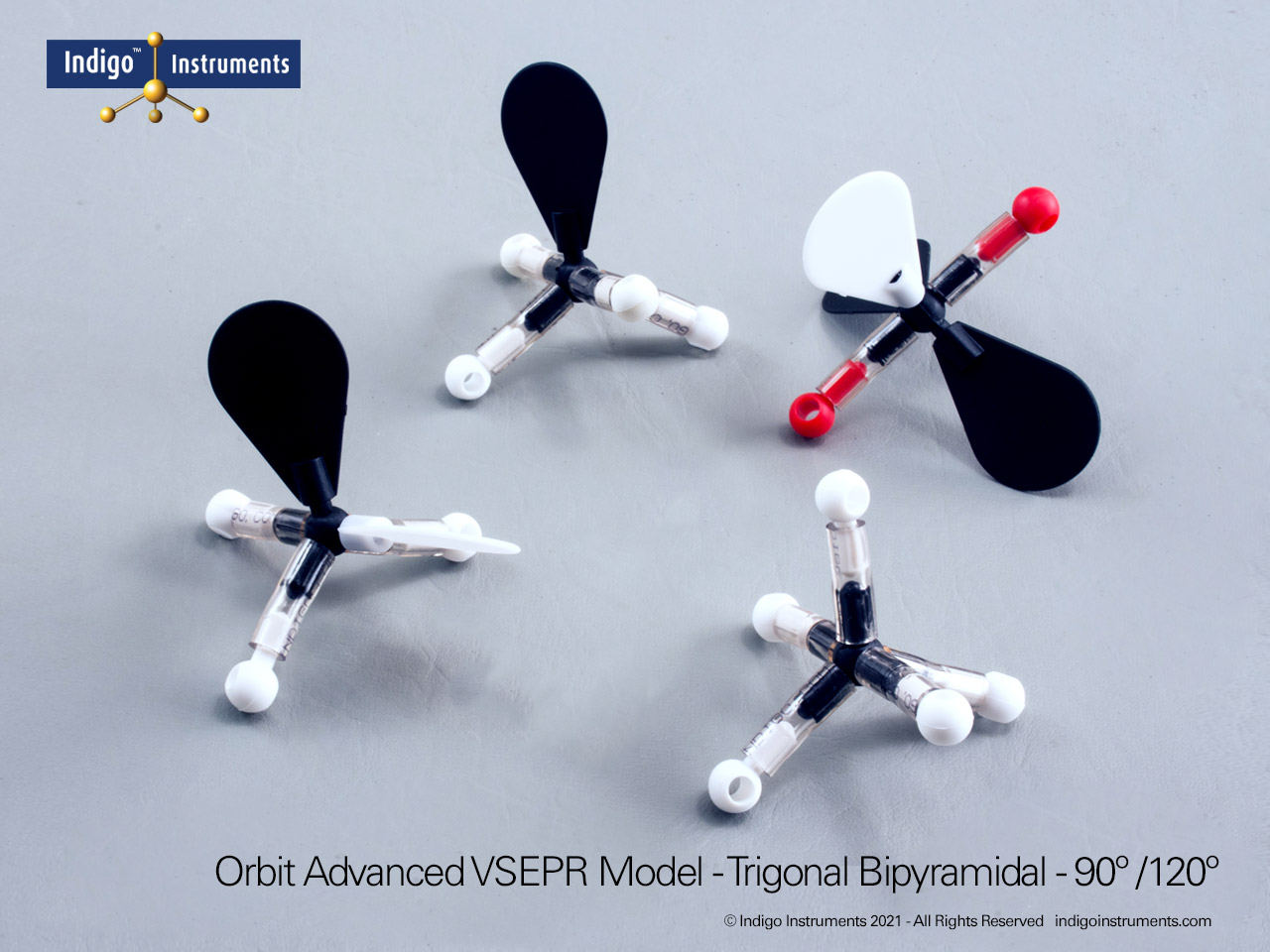
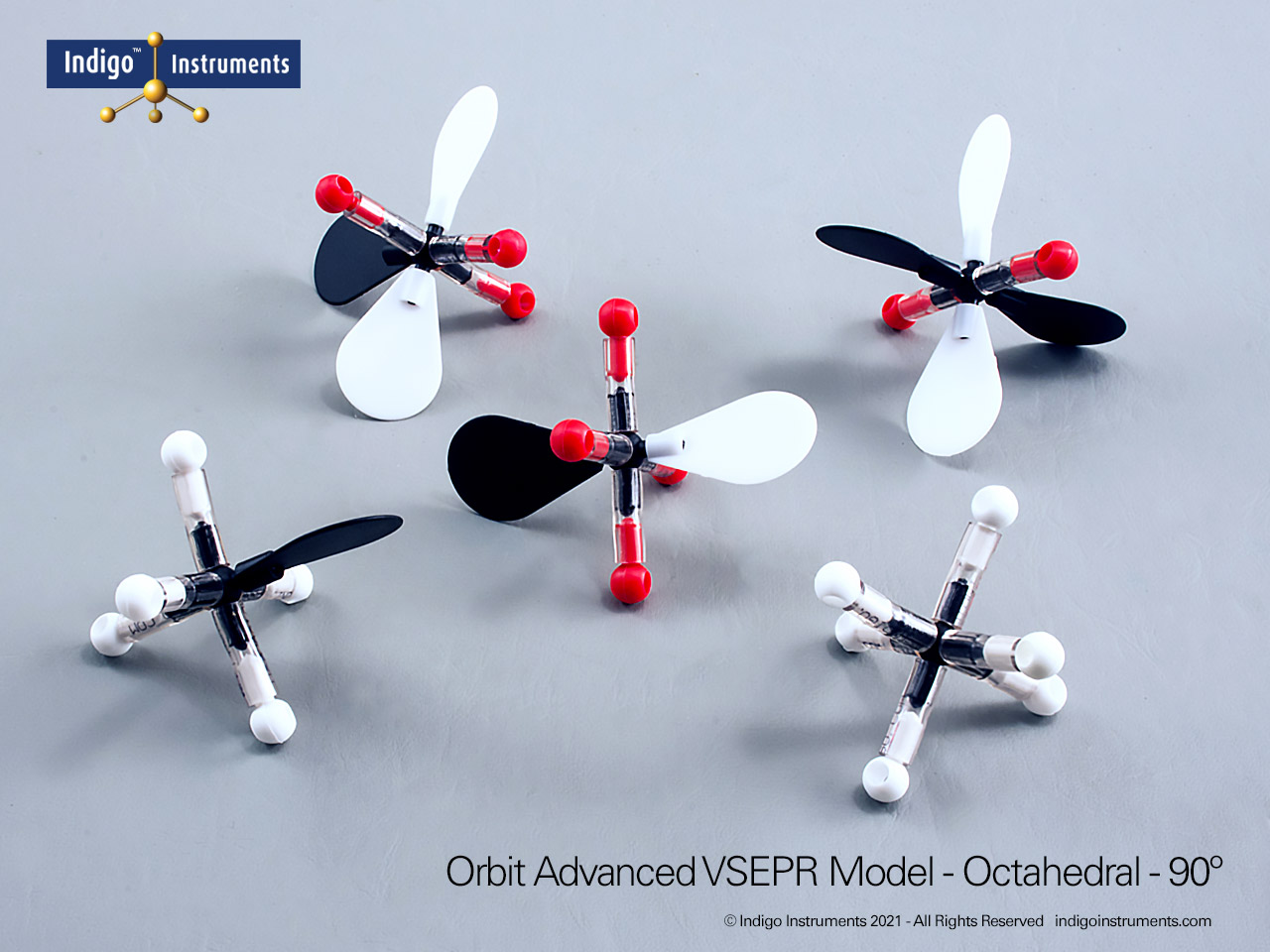
The Indigo®’s VSEPR theory model kit lets you visualize how electron-pair repulsion determines 3-D molecular structure. This advanced teaching kit shows fifteen distinct geometries, linear through octahedral, demonstrating how lone pairs and multiple bonds alter bond angles and molecular shape. Built from durable, autoclavable components, it’s ideal for advanced high-school and university chemistry courses exploring bonding, hybridization, and polarity.
The Indigo® VSEPR model kit helps students move beyond flat Lewis structures to hands-on 3D learning. Each molecular geometry model clearly shows how electron pair repulsion defines shape, linear, bent, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral. This molecular geometry kit is widely used in general chemistry and AP chemistry labs to illustrate bonding and polarity concepts that are difficult to visualize on paper. Whether you teach molecular shape, hybridization, or electron domain theory, this VSEPR model kit offers a durable, reusable way to demonstrate real molecular structures in three dimensions.
Learning Outcomes Table: 68823W VSEPR Model Kit
| Learning Goal | Description | Activity Example | Assessment Idea |
|---|---|---|---|
| Identify electron and molecular geometries | Distinguish between linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral arrangements. | Assemble each geometry and label bonding vs. lone pairs using different colored lobes. | Students match 3D models to Lewis structures or written molecular formulas. |
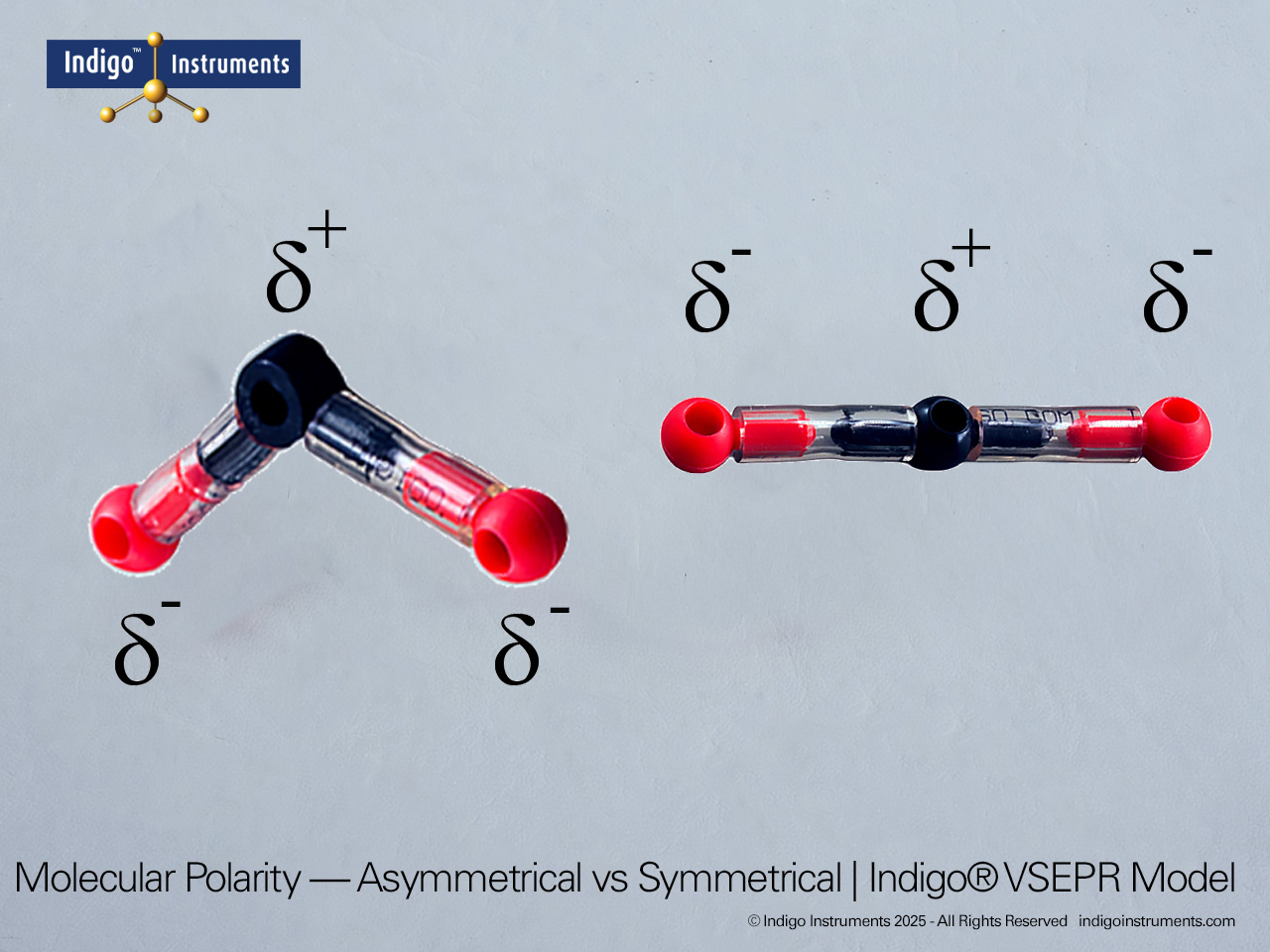
| Predict bond angles and molecular polarity | Use spatial arrangement to explain deviations from ideal angles due to lone pairs. | Compare tetrahedral CH?, trigonal pyramidal NH?, and bent H?O models. | Written short answer: “Explain why H?O is polar but CO? is not.” |
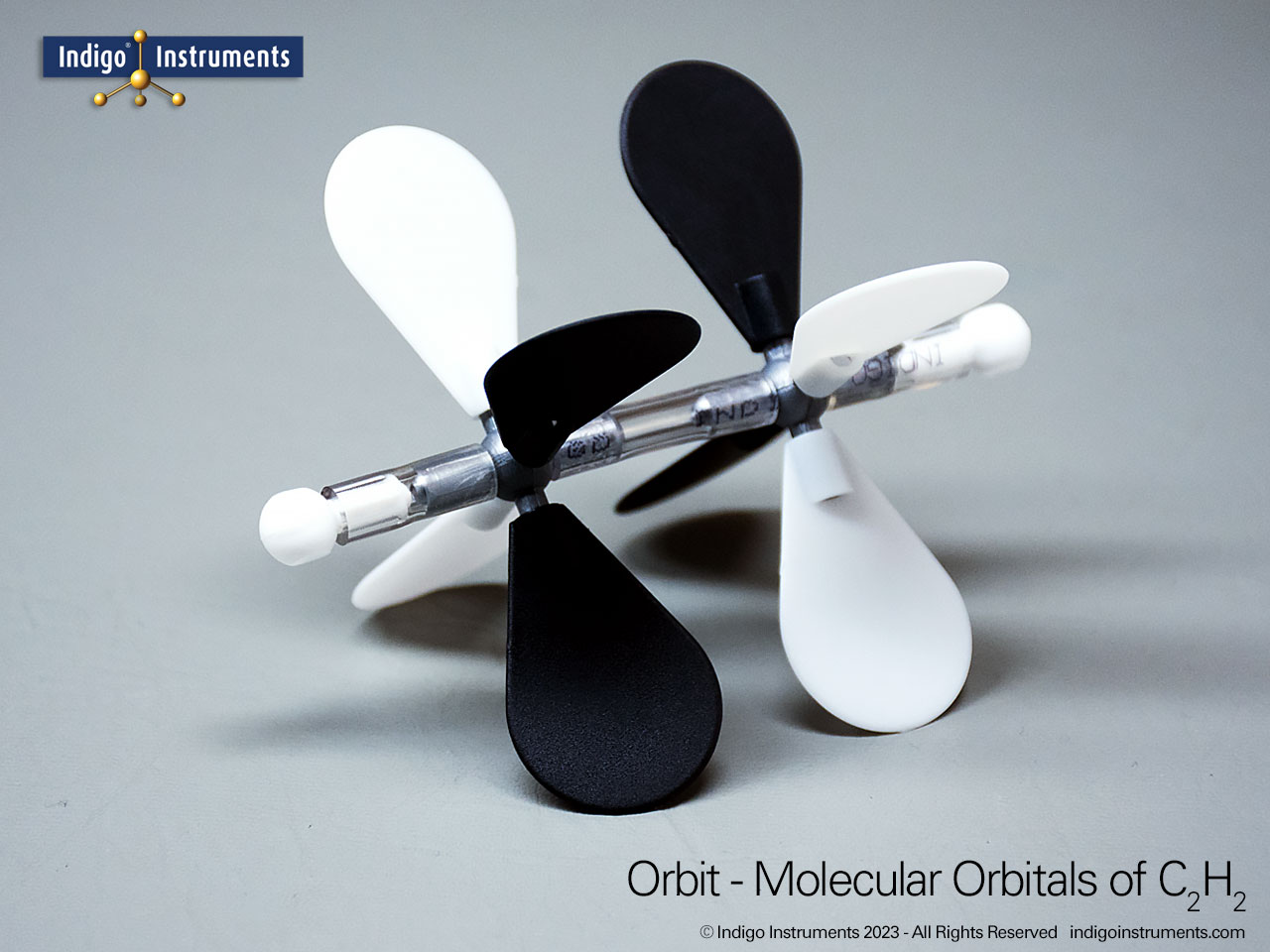
| Relate VSEPR theory to hybridization | Visualize sp, sp², and sp³ hybrid orbitals within each geometry type. | Build examples using linear (sp), trigonal planar (sp²), and tetrahedral (sp³) central atoms. | Label each model’s hybridization and justify with electron domain count. |
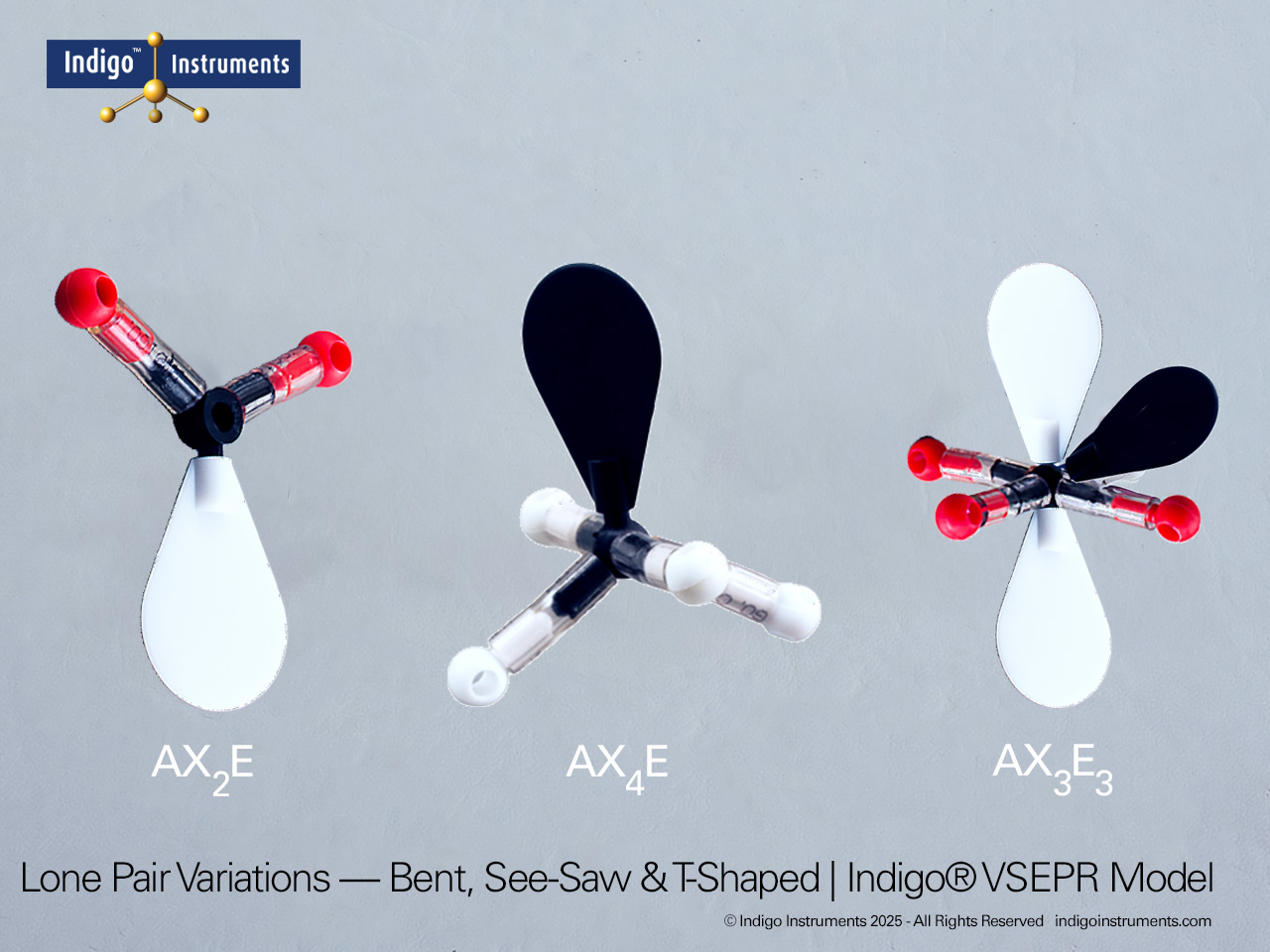
| Differentiate molecular and electronic geometry | Recognize that lone pairs alter molecular shape but not the underlying electron-domain geometry. | Construct SF?, ClF?, and XeF? to see trigonal bipyramidal variations. | Worksheet: draw both electronic and molecular geometries for given molecules. |
| Connect model visualization to real molecules | Relate abstract models to real chemical examples relevant to daily life and lab work. | Assign real compounds (CO?, NH?, SF?) for teams to model and present. | Group presentations comparing predicted vs. experimental bond angles. |