Indigo Dye Chemical Structure Molecule
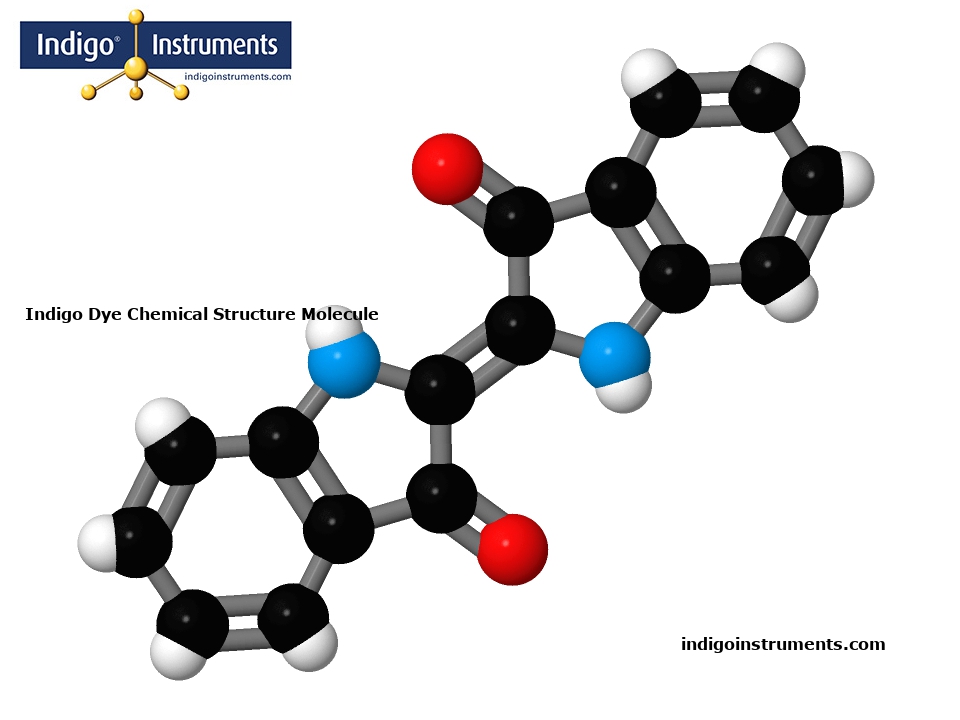
Build a molecular model of the Indigo dye chemical structure with genuine Molymod atoms & bonds. The model will show the core structure which is composed of two indole (benzopyrrole) units linked by a C=C double bond at the 2-position of each ring. Each indole unit contains a carbonyl (-C=O) and an amine (-NH-) group, forming lactam (-C=O-NH-) functional groups.
Indigo dye is a naturally occurring compound that has been been extracted from the leaves of plants such as Indigofera tinctoria and Strobilanthes cusia. Indigo pigments have dyed cloth made from silk, wool & cotton for thousands of years. The conjugated double bonds (contribute to its deep coloration) and form planar structures similar to the DNA nucleotides adenine & guanine.
The white light spectrum can be refracted by a glass prism into its constituent rainbow of colors. The spectral color Indigo describes wavelengths between blue & violet. The dye Indigo, more properly known as trans-indigotin absorbs light between the wavelengths of 375 to 475 nm with peak absorption at 437 nm.
Indigo Instruments was the world's original Indigo website going online in 1994.
A molecular model of Indigo Dye Chemical Structure Molecule in the Molymod Hybrid Dome style uses the atoms & bonds in the parts list below. Our free 3D Molecular Model Builder shows other styles & allows for image rotation as an assembly guide.
| Molecular Weight | Chemical Formula |
|---|---|
| 262.2672 | C16H10N2O2 |