Perovskite Gamma-Ray Imaging Device
SKU: 68790W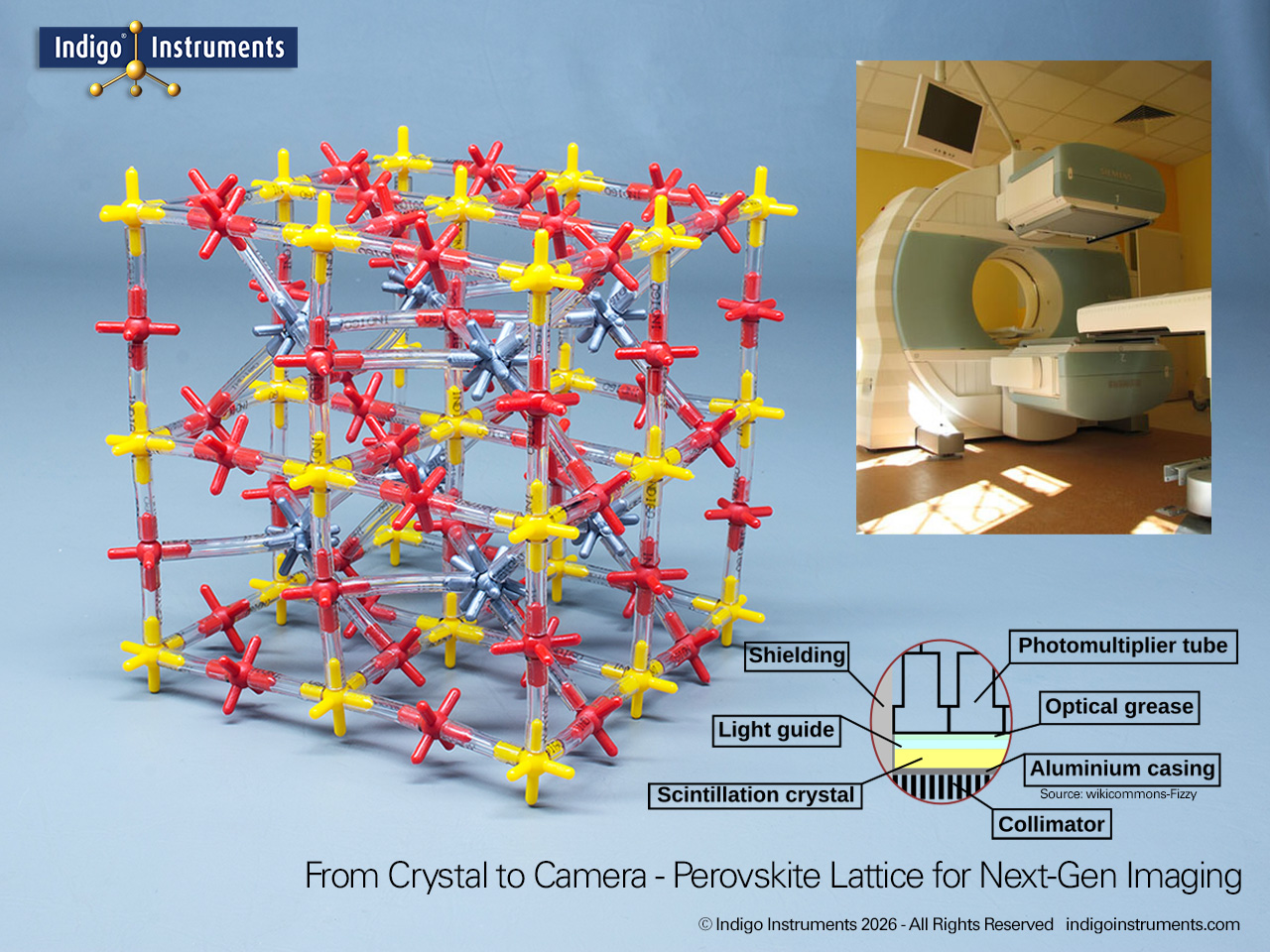
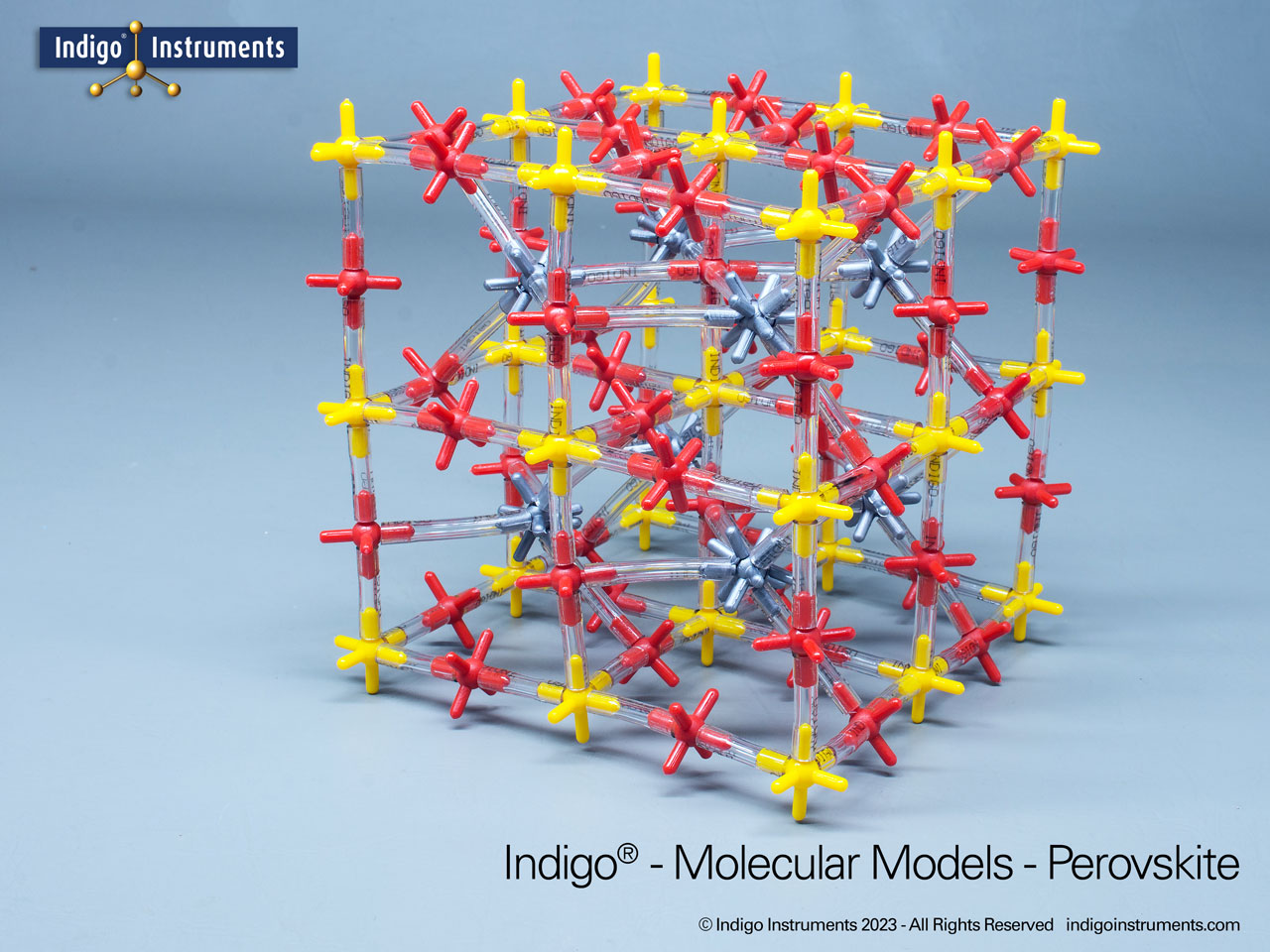
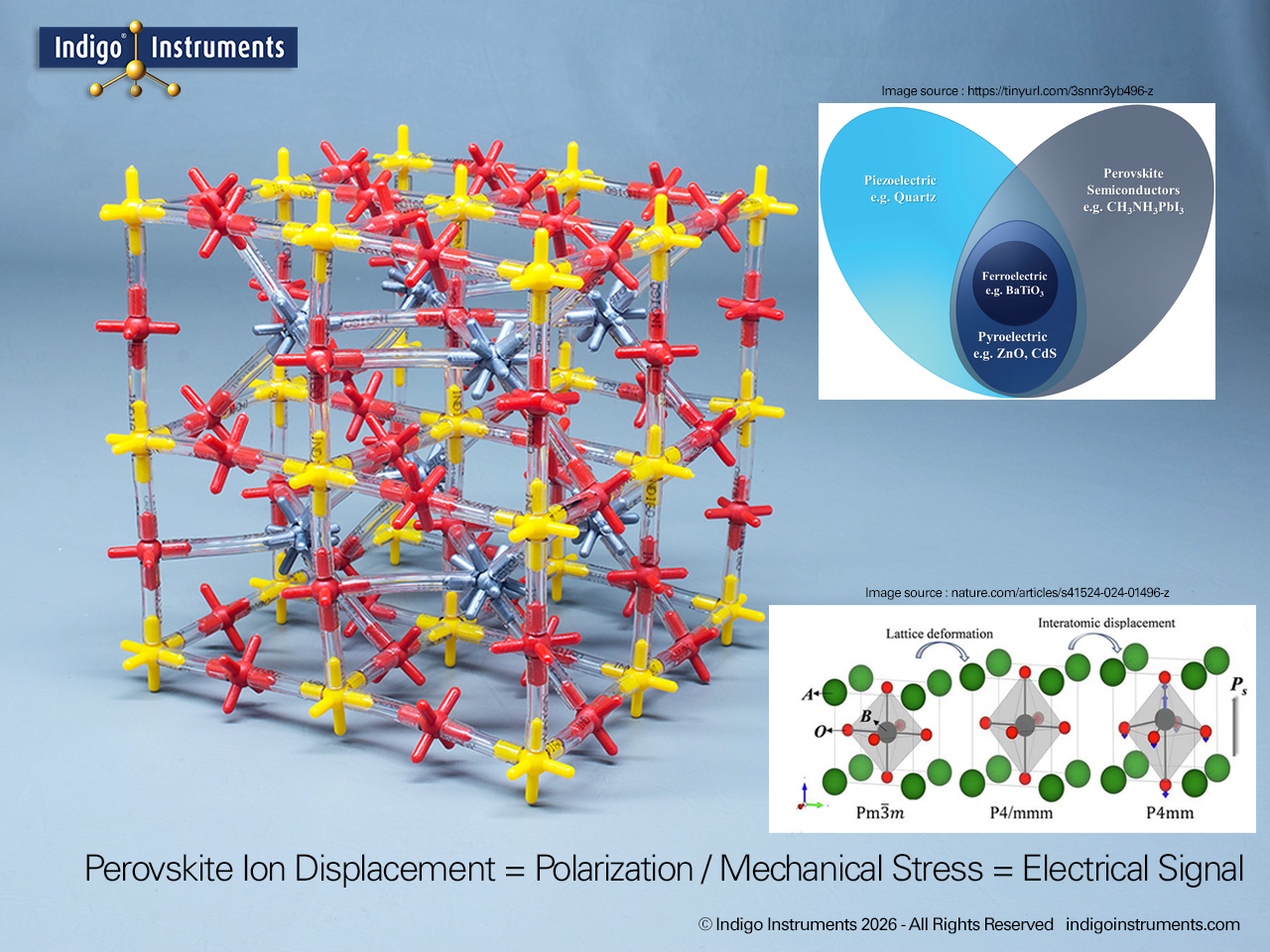
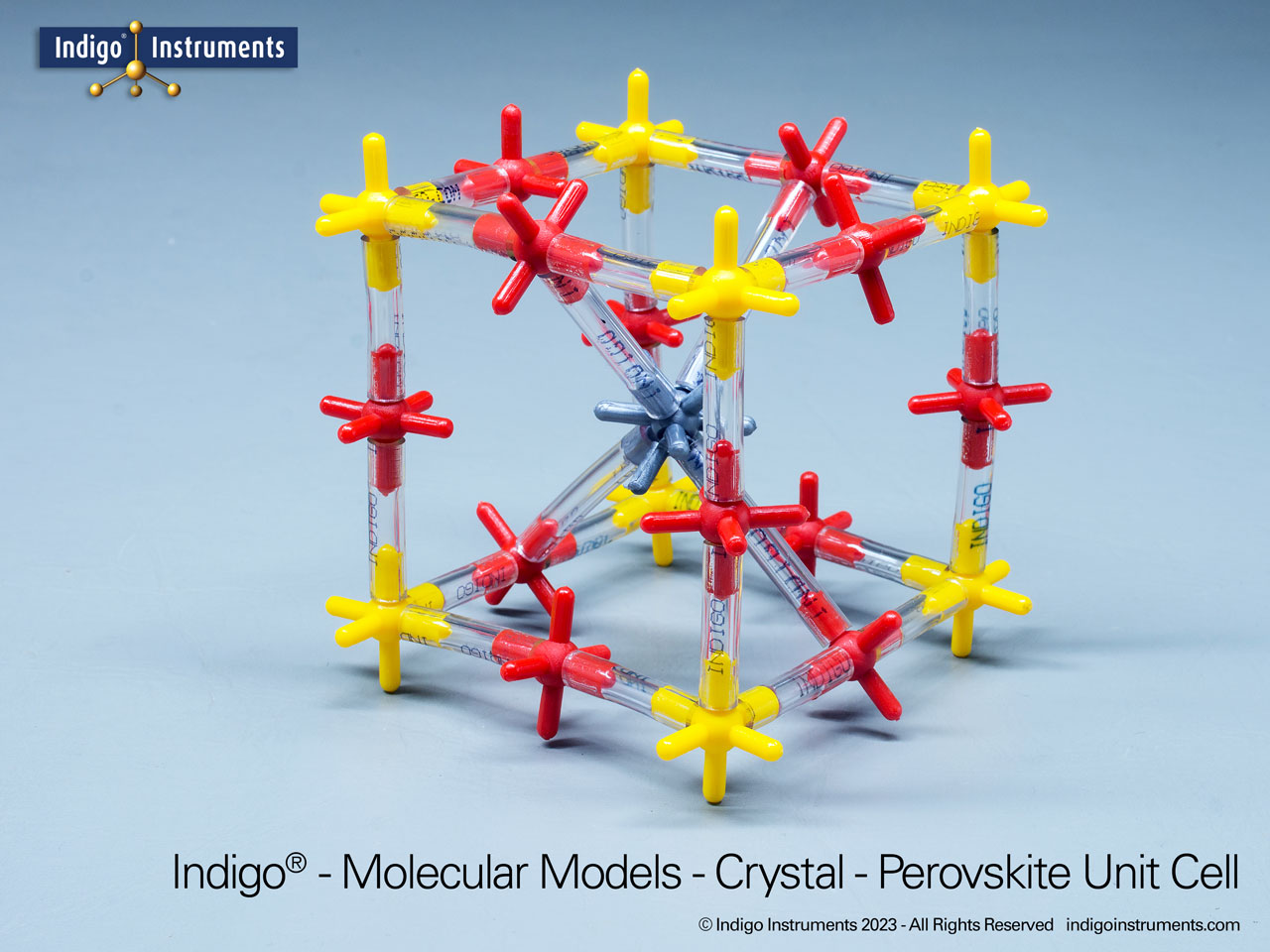
Investigate high-resolution gamma-ray imaging CsPbBr3 crystal based detectors with this Indigo® perovskite crystal lattice model. The potential of low-cost gamma cameras in medical diagnostics is a leap for nuclear medicine.
A breakthrough in medical imaging has emerged through the development of a perovskite-based gamma-ray camera. Using pixelated CsPbBr3 detectors behind a tungsten collimator, researchers have achieved single-photon γ-ray imaging with exceptional energy resolution and spatial detail. This innovation promises to reduce costs, improve image clarity, lower radiation doses, and make advanced nuclear medicine more accessible in clinical settings.
Unlike conventional gamma cameras that rely on expensive scintillators (NaI, CsI) or complex detectors (CZT), perovskite detectors offer a lower-cost, high-performance alternative. This new technology enables single-photon gamma-ray detection, imaging with perovskite semiconductors, and nuclear medicine applications of perovskite detectors. Early experiments show spatial resolution of ~3.2 mm and energy resolution of ~2.5% at 141 keV, rivaling existing commercial systems.
Indigo Instruments has maintained a substantial inventory of genuine Cochranes of Oxford (Orbit) parts for 30+ years (scroll down to see "Skeletal (Orbit/Minit) and are compatible with every molecular model kit we have sold since day 1. This level of quality may appear expensive but no parts support from other vendors costs even more.