7-hydroxyphenoxazone (Litmus)
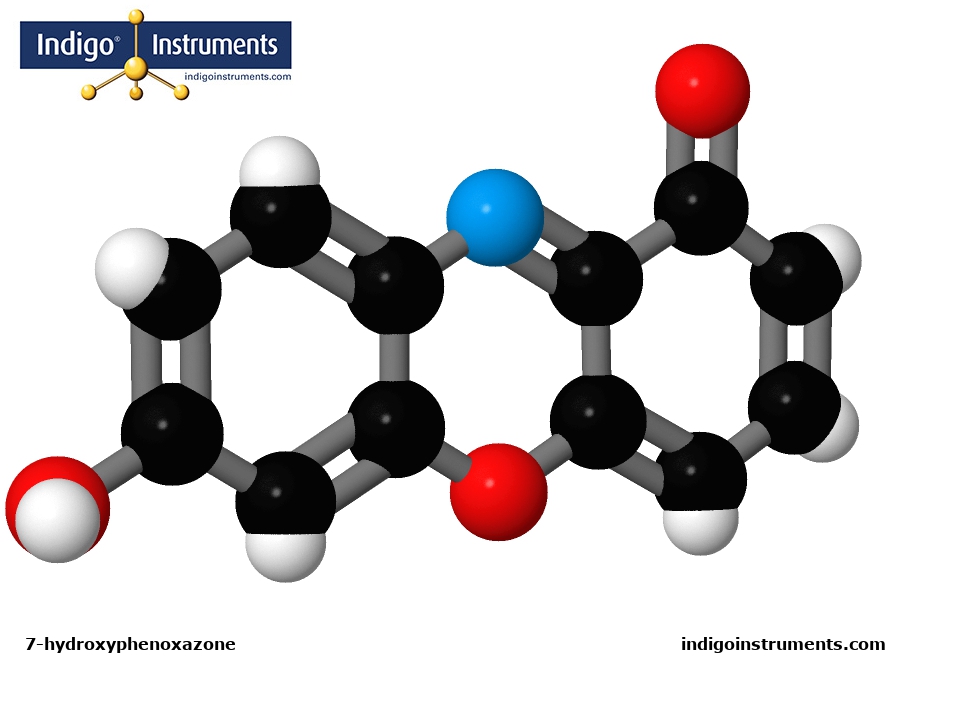
Build an acid base indicator litmus chemical structure molecular model of 7-hydroxyphenoxazone with genuine Molymod parts from Indigo Instruments.
7-hydroxyphenoxazone is the chemical compound used in litmus test papers as an indicator for acid, base or neutral pH of aqueous solutions. Structurally, it is a ketone. However, litmus is actually a polymer mixture of alpha-hydroxyorcein units linked together. 7-hydroxyphenoxazone is part of that polymer & acts as a chromophore by changing color.
The reaction indicating acid occurs when the nitrogen (blue N atom in image) in 7-hydroxyphenoxazone gains a proton (hydrogen, denoted by a white atom) which changes from neutral purple to red. Conversely, when exposed to alkaline media, 7-hydroxyphenoxazone loses a proton, from the OH (red-white hydroxyl group, lower left in the image) & changes from neutral purple to blue. These color changes occur in the pH range of 4.5-8.3 at 25o C. (Note that we do not supply purple-neutral litmus strips).
A molecular model of 7-hydroxyphenoxazone can be configured to physically show this. At pH7, the nitrogen atom has an unbonded electron pair. This can be denoted using a beige paddle to fill an empty hole in the blue atom. To indicate acidic pH, the paddle is replaced with a hydrogen atom, white "Molydome" atom & 2mm bond. (to match the style shown in the image). For alkaline conditions, the white hydrogen atom & bond are removed from the hydroxyl (OH) & replaced with a beige paddle. (Note the parts list below does not include any beige paddles)
This can also be demonstrated physically with Indigo® Litmus Test Strips & Sheets.
A molecular model of 7-hydroxyphenoxazone in the Molymod Hybrid Dome style uses the atoms & bonds in the parts list below. Our free 3D Molecular Model Builder shows other styles & allows for image rotation as an assembly guide.
| Molecular Weight | Chemical Formula |
|---|---|
| 213.1922 | C12H7NO3 |