LSD Chemical Structure Model-Assembled
SKU: 62208A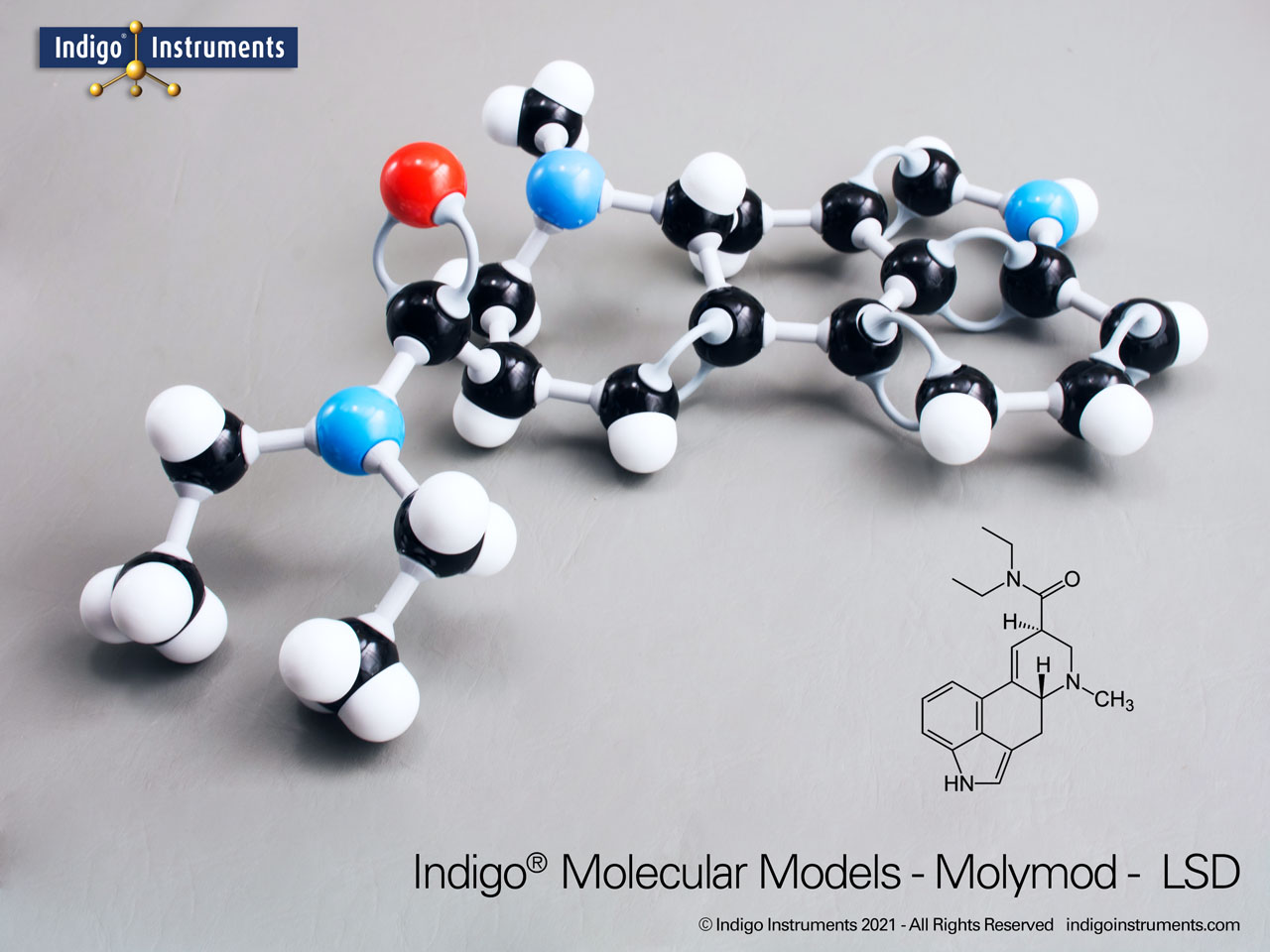
The full chemical name of LSD is lysergic acid diethylamide. It belongs to a group of compounds known as indole alkylamines or substituted tryptamines & is characterized by its amide and carboxylic functional groups.
LSD is also a very good example of the importance of stereoisomerism. D-LSD is the active form while its mirror image, L-LSD (L-lysgeric acid diethylamide) does not induce hallucinations. Compare LSD's structural similarities to neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine.
You can also use this model to compare LSD's molecule structure to other psychotropic compounds such as mescaline & psilocin as part of your drug awareness program.
Why educators choose Indigo® Instruments models? We've kept inventory of genuine Molymod atoms & bonds for 30+ years; compatible with every molecular model kit we have sold. This level of quality may seem expensive but no parts support from other vendors costs even more.