PTFE (Teflon)
Construct a 3D molecular structure model of the non-stick coating polymer PTFE (Teflon) using Authentic Molymod Model Parts by Indigo
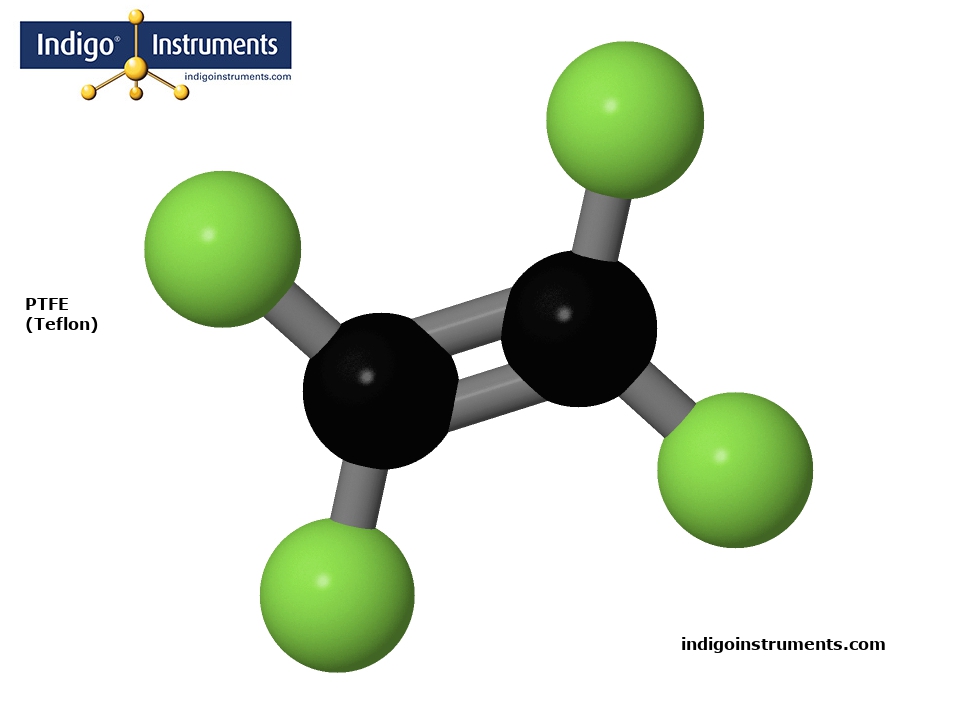
Tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) is the monomer subunit of PTFE/Teflon shown in the image. It is a simple fluorocarbon consisting of two carbon atoms double-bonded (C=C) to form an alkene backbone along with 4 fluorine atoms that replace the hydrogens in ethene (ethylene). This chemical configuration makes TFE highly electronegative, chemically stable, and hydrophobic.
TFE readily polymerizes to PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), better known as Teflon. The TFE polymerization to form PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) involves a free radical initiator like a peroxide which breaks the C=C double bond. Propagation proceeds in a chain reaction that extends the polymer backbone & ends when a terminating reaction occurs. In effect, the alkene double bond is replaced by single bonds which form a long, strong carbon-fluorine polymer chain. C-F bonds are particularly strong making PTFE highly non-reactive and thermally stable.
For those with an aversion to chemicals, the non-stick feature of teflon can be achieved by high temperature alone, see Leidenfrost Effect
A molecular model of PTFE in the Molymod Hybrid Dome style uses the atoms & bonds in the parts list below. Our free 3D Molecular Model Builder shows other styles & allows for image rotation as an assembly guide.
| Molecular Weight | Chemical Formula |
|---|---|
| 100.0156 | C2F4 |